Just like you say tomato and I say tomahto, internet vs intranet are the same, right? Although the names sound similar and share several features, the platforms have distinct differences. Here, we debunk some of the confusion and provide simple-to-understand explanations. You will have a better understanding of how each platform works and the different ways they add value to businesses. Ready to find out the differences between the internet vs intranet? Let’s dive in.
What Is The Internet?
You already know what the internet is. After all, it’s an everyday part of our lives. We use it for communication, entertainment, news, and accessing social media platforms. From banking to shopping and booking flights, we also use the internet to manage our lives. Most of us take the internet for granted. But how does it all work?
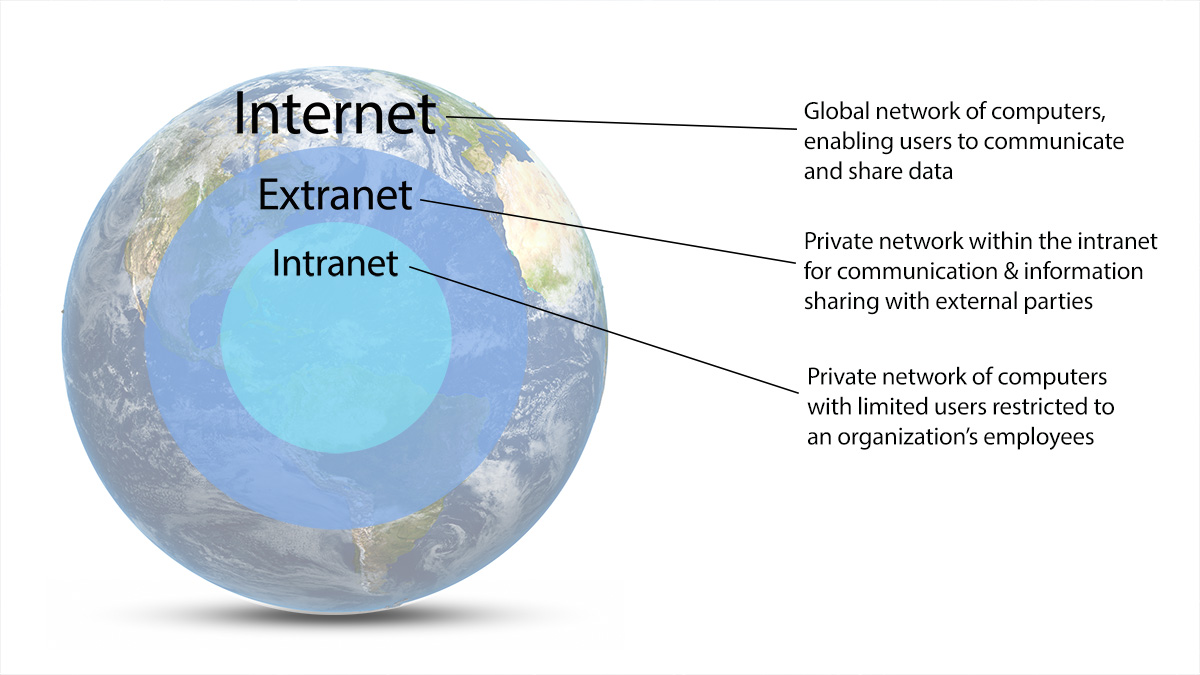
The internet is a global computer network to facilitate communication and share information. It uses both wired and wireless communication (Wi-Fi, ethernet, and cable, plus 3G and 4G) to send and receive data.
The internet is a public computer network accessible to anyone. Currently, there are 5.35 billion active internet users worldwide, around 66 percent of the world’s population.
No one organization oversees the internet. Every computer has its own internet protocol (IP) address. And the IP identifies the computer’s location within the global network. A series of rules and standards known as protocols connect the various networks. Web browsers such as Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge provide access to the world wide web.
How Do Businesses Use The Internet?
Companies use the internet in much the same way we do outside work. Business emails, banking, research, and communication all happen over the internet.
However, your company website is also the public face of your organization. It’s used to buy or sell products and services, engage in online marketing, and connect with customers and prospects. Plus, companies use the internet to monitor what the competition is up to.
What Is An Intranet?
Unlike the internet, an intranet is a private network of computers owned by an organization. Only authorized users with the correct login credentials can access resources on the intranet. Users can’t just stroll in and check out what’s happening. So, think of the intranet as a privatized version of the internet, exclusive only to company employees.
The company’s intranet connects employees and is used to share data, communication, and information within the business.
Both platforms use the same hardware, including routers, servers, and data network cables. They also have similar architectures and data-sharing protocols.
Furthermore, intranet sites look and act like other public websites. However, they tend to be more task-focused than the promotional company internet site. Intranets are designed to solve business challenges within an organization, from internal communication to collaboration or knowledge sharing. Simply put, intranets are a central digital hub where staff go to get things done.
Your intranet site can be hosted on a company server. However, nowadays, most intranets are cloud-hosted, allowing for any time, anywhere access – perfect for hybrid and remote working.
Security is a crucial feature of intranets. The internet is notoriously vulnerable to hacking and privacy breaches. By contrast, your intranet is a secure network protected by a firewall and the latest two-way SSL encryption. You can have complete confidence that your data is safe and secure.
How Do Businesses Use An Intranet?
Intranets first arrived on the digital scene back in the 1990s. And you may well have encountered one of the early versions. Often dismissed as dull, clunky document libraries, intranets got a bad rap.
However, the technology has evolved, and today’s company intranet is a flexible, versatile platform your employees will love. Plus, the setup is super easy. You won’t need a computing degree to get started.
Intranets are crucial in connecting employees and facilitating information sharing, internal communications, and much more. Intranets are designed to address business challenges. Here are just some ways organizations use intranets to do just that.
Improve Internal Communication
Connecting employees is always a challenge, whether your people are in one office block or spread worldwide. Intranets make that task much easier. Company news and updates are shared on the dynamic intranet newsfeed.
Furthermore, most intranets allow workers to set their own communication preferences with notifications and alerts. This is empowering for your people, and it cuts down on information overload.
Smarter Team Collaboration
Using email and apps for collaboration is not the most efficient way to get things done. And it can even be a security risk. Cut the clutter with a secure internal network. Project forums, private messaging, and IM threads streamline collaboration and boost productivity. You can even integrate your intranet with cloud solutions like Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Salesforce for enhanced secure collaboration.
Streamline Business Processes
The intranet’s online workflows and processes will save you time, hassle, and money. Whether booking vacations, ordering supplies, or approving purchase orders, intranet software is faster and more accurate.
Better Knowledge Management
Your intranet provides a single source of truth for all critical company knowledge. You can remove departmental silos with a centralized and searchable knowledge management database. Everything staff need to know, from SOPs to handbooks and policies, is accessible to all, including on-the-go and remote workers.
Enhanced Employee Engagement
Modern intranets come packed with social features to improve employee engagement. Activity walls, follows, hashtags, and emojis mirror social media platforms staff already use. Everyone is updated with personalized newsfeeds, trending #channels, and company blogs. Plus, intranets help you identify what workers really think with pulse surveys and snap polls. Connecting and engaging with employees is a whole lot simpler with an intranet.
The bottom line is that intranets help organizations stay connected, productive, and secure. And because they are cloud-based, all employees can take advantage of these digital workspaces.
Can An Intranet Work Without The Internet?
The answer is yes and no. Early versions of the intranet were local area networks hosted on private servers, making them almost separate from the internet.
However, these days, most intranets are cloud-hosted and can only be accessed using an internet connection. This offers several advantages, including any time, anywhere access, making it the preferred solution for today’s hybrid workforces.
What Is An Extranet?
You may have also encountered extranets and wondered how they fit into the mix.
An extranet is an extension of your intranet for authorized external users—think customers, vendors, or partners. These external parties can access specific resources within the full intranet.
An extranet is still a secure private network and requires an internet connection. It uses the same protocols and hardware as the internet and intranet. Security measures like firewalls and password-protected logins provide controlled access and allow you to collaborate securely and share information. You still manage the site and its content and control who has access, although you can choose to share oversight with your partners.
For example, you have a customer who places regular orders with your company. Setting up an extranet means they can update orders, process invoices, and chat with the team. Improved customer service and satisfaction are obvious spinoffs.
How Do Businesses Use An Extranet?
Here are some other examples of how organizations use an extranet.
- Improve communication between suppliers and distributors in a distribution network.
- Faster file sharing with external partners’ connected devices.
- Easier collaboration and communication for franchise interconnected computer networks with locations across several states or countries.
- More efficient project management with subcontractors and stakeholders.
- Better cross-team collaboration between government agencies.
- Secure exchange of inventory data in an e-commerce site integration.
- Customer portals for order monitoring, access to product information, and quick resolution of queries.
- Improved onboarding for freelancers or contractors who don’t have access to the complete intranet.
- Creating a customer community to share product updates and special offers.
Is A VPN An Intranet Or Extranet?
A virtual private network (VPN) securely connects different parts of intranets and extranets. However, it doesn’t neatly fit into either category. Instead, a VPN establishes encrypted connections over the internet, creating a protected private network between two or more devices. This enables data transmission through virtual channels while bolstering security and preventing breaches.
Which Is Better, Internet vs Intranet Or Extranet?
Of course, the internet is vital for every business. With billions of users worldwide, your organization needs an online presence to showcase products and services to limitless potential customers. As a marketing tool, the internet is without parallel. Plus, the internet is essential for keeping on top of industry news, networking with like-minded professionals, and tracking the competition.
However, the internet has its limitations when it comes to business operations. The main disadvantage is that you have no ownership or control. After all, the internet is a public network accessible to everyone. Plus, cybersecurity is an issue. Hackers and fraudsters thrive in the open, unregulated world wide web.
Intranets are a boon for safe and secure business operations. They offer all the advantages of the internet for fast communication and data sharing without the security drawbacks. The company intranet is a local private network under your control and ownership. Firewalls and password-protected sign-in safeguard critical company information. Your people can connect, collaborate, and communicate in a completely secure environment.
Although extranets are not relevant to every business, they offer the same degree of control and security as intranets. This makes extranets a great option if you regularly collaborate and share data with external parties.
Differences Between Interner vs Intranet
Here’s a handy table summarizing all the key differences we have covered.
| Feature | Internet | Intranet | Extranet |
| Name | Inter means between | Intra means within | Extra means outside |
| Definition | Global network of computers, enabling users to communicate and share data | Private network of computers with limited users restricted to an organization’s employees | Private network within the intranet for communication & information sharing with external parties |
| Purpose | Provides information & communication technology to all connected users | Solves business problems, delivers safe and secure internal communication & data sharing | Improves collaboration & flow of information between an organization & third parties |
| Network Access | Open access | Accessible only to employees | Restricted access on a need-to-know basis |
| Type of Network | Insecure, vast network with multiple users – the network of networks | Closed, secure network between an organization’s workers – relies on the internet to work | Closed, secure network between an organization & selected external parties – depends on the intranet to work |
| Ownership | None | Owned by the organization | Owned by the organization or shared with third parties |
| Data Exchange Capabilities | Can transfer unlimited data | Can transfer only limited data | Can transfer only limited data |
| Information | All types of information are freely available on the internet | Data is limited to company-specific information | Data is limited to extranet-specific information |
| Security | Relies on the internet user to secure their network | Enforced by the organization with firewalls & password protection | Enforced by the organization with passwords & firewalls, which separate the extranet from the intranet |
| Regulation | Unregulated | Regulated by the organization with policies & procedures | Controlled by the organization or in partnership with third parties |
| Users | Unlimited | Employees within an organization only | Limited to employees of all connected organizations |
Similarities Between Internet Vs Intranet And Extranet
Despite the differences, several features are standard to all three networks. Here are the headlines:
- Network Technology: They all use internet protocol to transmit data between computers connected to a network.
- Web Technologies: They can apply Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to deliver web pages and online services.
- Web Browsers: Users obtain information on all three networks using online browsers.
- Data Transmission: Each network type involves data transfer between connected devices.
- Security Protocols: Each network has security measures for safeguarding sensitive communication.
Internet vs Intranet Round-Up
Intranet, internet, and extranet may sound the same. However, they are different beasts when it comes to operating your business. They all use similar technology to facilitate communication and information sharing. However, security is the fundamental difference between the internet and the other computer networks. The internet is an unregulated, open public network. By contrast, the intranet and extranet provide a secure private network.
Companies’ needs vary based on their size and industry. Smaller ones may deem an extranet unnecessary if they have limited partnerships, while medium-sized companies can benefit significantly from an extranet for collaboration and customer service. Conversely, large companies with complex workflows and numerous business relationships require all three networks to meet their diverse needs.
In specialized fields like healthcare and finance, where security and privacy are critical, having an intranet, internet, and extranet provides comprehensive protection and efficiency. As hybrid work arrangements become commonplace, intranets and extranets play a pivotal role as mission-critical tools for organizations. Companies must carefully assess their unique requirements and operational dynamics when deciding whether to use intranets, the internet, and extranets in their network infrastructure.
About MyHub
We are a leading intranet software provider. Our modern intranet solution brings your people or selected authorized users together. Share resources, connect, and communicate in a controlled private network.
Find out more with MyHub’s free demo or 14-day no-obligation trial.








0 Comments